Tuesday, June 14, 2011
B.E.D.M.A.S
E - exponents
D - Division
M - multiplication
A - addition
S - subtraction
Solve this problem:
(34.67+23.65) x 5.6 -:- 11.2 =
check:
(34.67 + 23.65) x 5.6 -:- 11.2=
58.34 x 5.6 -:- 11.2=
326.704 -:- 11.2=
29.17=
Math Review
Translation- slide along a straight line
Rotation- turn about a fixed point
Reflection- mirror image
Know how to do and describe each of them
plot (-4, 6) on this grid. Sorry if the grid is too small.
Notes
- The most frequently occuring number in a set of data.
- The sum of a set of values divided by the number of values in the set.
- The positive difference between the largest and smallest values in a data set.
- A value that is much larger or smaller than the other data value.
Math Exam Review(BEDMAS)
B= Brackets
E= Exponents
D= Division
M= Multiplication
A= Addition
S= Subtraction
Here is a video that can help you:
Notes for June 6, 2011
- a value that represents the center of the data set.
- can be mean, median, or mode
Data set - is a group of numbers that you must arrange in order from least to greatest.
data set- 2, 3, 4, 5, 4, 5, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 5, 34, 3
arrange- 2, 3, 3, 3, 4, 4, 4, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 6, 6, 7, 34
Median- the middle number in a set of data after the data have been arranged in order.

Mode- the most frequently occuring number in a set of data.


Range- the positive difference between the largest and smallest values in a data set.

Outlier- a value that is much larger or smaller than the other data value

Practice
Find the mean, median, mode, range and outliers
- 45, 2, 48, 40, 45
- 14, 15, 18, 98,
- 100, 45, 110, 100, 150
Here is a video about measuring central tendency
Math Review Exam Slide 22


Math Exam Review (Last Page)

 Sorry the answers to the questions was small.
Sorry the answers to the questions was small.June 6th Notes
-a value that represents the centre of a data set
-can be the mean, median, or mode
-data set is a group of numbers that you must arrange in order from least to greatest
eg. 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 5, 4, 5, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 5, 34, 3 (not organized)
2, 3, 3, 3, 4, 4, 4, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 6, 6, 7, 34 (organized)
- Median- the middle number in a set of data after the data have been arranged in order

- Mode- the most frequently occurring number in a set of data
-mode of 3, 5, 7, 7, 9 is 7
-mode of 2, 2, 4, 6, 6, 8, 11, is 2 and 6 (can have more than 1 mode)
- Mean- a measure of central tendency
-mean of 6, 4, 8 is 6 (6+4+8= 18/3= 6)
-add up all the numbers, divide by how many numbers there are
- Range- the positive differences between the largest and smallest values in a data set
-range of -7, -4, -2, -1 is 6 (-1) - (-7)= 6
- Outlier- a value that is much larger or smaller than the other data value
-outliers for 1, 64, 65, 67, 67, 68, 100 are 1 and 100
Here is a link to a math game:
http://ca.ixl.com/math/grade-7/calculate-mean-median-mode-and-range
Here is a math video, ENJOY!
Math Exam Review (Page 6)

Always remember when you're adding and subtracting fractions, you should always simplify (put it into lowest terms)


Here is a LINK of where you can learn facts about divisibility
But, If you want to learn about Adding and Subtracting fractions, here is also a LINK.
Math Exam Review (Page 1)
Translation- A slide along a strait line
Rotation-Turn about a fixed point
Reflection-Mirror Image


Quadrant I (+,+)
Quadrant II (-,+)
Quadrant III (-,-)
Quadrant IV (+,-)
Adding, Subtracting, Multiplying, and Dividing decimal numbers using a calculator. Here are some exercises you can try with your calculator. (I just made those up, because we already did the examples in class)
1.)43.12 + 65.23 + 9.01=
2.)24.576 - 23.07=
3.)6.05 x 87.32=
4.)71.08 ÷ 12.04=
Math Exam Review Slide 23

So the question is 1/2+1/2 = 2/2, but that isn't good enough because you have to always simplify when it can be simplified. So its 1/1 then 1 whole. First you always check for common denominators. If your fractions have the same denominator you leave them the same and just add the numerators.
Subtracting

The question was 3/4 - 1/4=2/4=1/2. ( make sure you don't forget to simplify.) First you check for common denominators. In this question they are the same so just take away the two numerators.
Try these questions to help you practice :).
2/3+4/5=
6/7+2/8=
2/3-1/3=
4/5- 2/5=
Answers...
1. the common denominator is 15. So whatever you did to get 15 u do to the numerators. So 2x5=10 so its 10/3, then 4x3= 12 so its 12/5. So 10+12 = 22 and the denominators stay at 15. Its 22/15. Now you have to simplify it to 1 whole and 7/15.
Since I already told you how to do this I'm just gonna give you the answers now.
2. 1 whole and 3 /28
3.1/3
4. 2/5
Here is a link to help you. :)
GoAnimate.com: Adding and Subtracting fraction by soto
Heres a video to help you (:
Friday, June 10, 2011
social studies answers
Chapter 1 Terminology Name________________
1. Middle Ages p24 -the time period lasting 1000 years between the 5th century and the 15th centuries
2. antipodes p26 - points on the opposite sides of the earth.
3. equator p26 - the imaginary line around the centre of the earth half way between the North and South poles( called 0 degrees latitude).
4. poles p26 – the North and South points at either end of the earth’s axis.
5. Compass Rose p26 - a tool to find direction used on maps (shows North, South, East and West).
6. axis p26 – an imaginary line that goes through the centre of the earth between the North and South poles.
7. rotation p26 – the earth spinning on its axis.
8. revolution * old text p 31 - the movement of one planet around another planet/star
e.g. the Earth around the sun
9. orbit*old text p 31 – the path any planet follows around the sun
10. leap year*old test p 31 – every 4th year that has 366 days to make up for the previous 3 at 365 1/4 days.
11. equinox*old text p 33 – twice a year when the daylight hours equal the night hours.
12. solstice * old text p 33 – twice a year when either the daylight or nighttime are at their maximum.
13. latitude/parallels p28 – imaginary lines that run from East to West that are used the show distance from the equator.
14. longitude/meridians p29 -– imaginary lines that run from North to South that are used the show distance from the Prime Meridian.
15. Prime Meridian/ Greenwich p29 – an imaginary line of longitude running from the North
poles to the South pole used to judge time and distance.
16. sundial p 30 - an ancient tool for measuring time using the movement of the sun.
17. time zones p31/33 – are the system for keeping time around the world that has each hour of
the day equal to 15 degrees longitude.
18. International Dateline p31 – an imaginary line of longitude that is opposite the Prime Meridian.
19. Global Positioning System p34 – technology that uses information from satellites to find absolute location of people or things.
20. map projections – ways of showing the earth ( a sphere) which is three dimensional as a flat
map which is two dimensional.
21. continent p2- - any of the seven large land masses.
22. island p3 - land that is surrounded by water.
23. peninsula p4 -a piece of land jutting out into the ocean from the mainland surrounded by
water on three sides.
24. topography p4 - the surface features of the earth such as mountains, hills, plateaus and plains.
25. mountain p4 - a high rugged landform.
26. valleyp4 - a lower area of land formed by erosion that has elevated land on both sides.
27. plain p5 -ia broad flat or gently rolling area of land.
28. plateau p5 - a broad flat or gently rolling area that is higher (elevated) above its
surroundings.
29. elevation p5 - the distance or height above sea level.
30. riverp6 - a natural channel of water flowing toward a lake or ocean.
31. tributary p6 -a small stream flowing into a river which may flow into a lake or ocean.
32. lake p6 - a body of water surrounded by land.
33. gulf p6 - formed when the ocean makes a large indent into land forming a semi-circle
34. strait p6 - a narrow channel of water connecting two larger bodies of water.
35. Pangaea p10 - the name of a supercontinent that existed of 200 million years ago.
36. fossil p10 - the remains of plant or animal found in rock.
37. tectonic plate p11 - a large piece of the Earth’s crust that can be bigger than a continent.
38. rift p11 - a split in the Earth caused by tectonic plates pulling away from each other.
39. erosion p18- - the action of wearing away of the Earth’s surface by air, water and ice
40. deposition p18 - the relocation of soil and pieces of rock that were worn or carried
away by wind, ice, and water.
41. silt p19 – small pieces of soil and rock carried by water.
42. delta p20 - a triangular shaped deposit of soil and sand at the mouth of a river.
43. glacier p20- - a gigantic body of ice that is found in mountain and polar regions.
44. geography - study of our world
45. geographer -person who describes and analyzes the human and physical characteristics of the world
46. absolute location -the exact location of something on the earth using coordinates of latitude and longitude
47. scale - the ratio between the real distance and the distance on a map
48. Geography Information System technology to display and store facts about the physical world
Chapter 2 and 19 Terminology Definitions Review for Climate and Sustainable Development
49. physical geography The study of the natural features of the earth
50. hemisphere A half-sphere view of the earth created by geographers to identify a large part of the earth e.g. northern, southern, eastern or western
51. landforms A particular land surface feature, such as a mountain, hill, plateau, or plain
52. hills An elevated piece of land
53. ocean currents Water flowing by continents which either warm or cool the land based on their temperature.
54. volcano Outward explosion of the earth’s molten inner core caused by tectonic forces
55. weather The day to day temperature and precipitation found anywhere in the world.
56. Mid-latitude Climate located from 30 to 60 degrees latitude North or South of the equator.
57. prevailing Winds that blow in a specific pattern around the earth.
58. humid When there is a lot of moisture in the air.
59. transpiration Water vapor from plants.
60. arid Very dry, little or no precipitation.
61. permafrost Permanently frozen ground, about 1 meter beneath the surface.
62. Air mass A large body of air covering a large distance.
63. precipitation Water (in any form) falling to Earth.
64. climate Pattern of weather in a particular place measured over at least 30 years.
65. Low latitude Climate located from 0 to 30 degrees latitude North or South of the equator.
66. hydrologic The name of the cycle of water through land, water and air.
67. condensation Water vapor changes from a gas to a liquid.
68. Water vapor An invisible gas created when water evaporates.
69. leeward Mountain slopes that face away from the prevailing wind.
70. orbit A circular path a planet like Earth takes around the sun.
71. altitude The height of any part of the earth above sea level.
72. evaporation Water changes into a vapor or gas.
73. High latitude Climate located from 60 to 90 degrees latitude North or South of the equator.
74. tropics Area between the Tropic of Cancer and Tropic of Capricorn.
75. windward Mountain slopes that face the prevailing winds.
76. atmosphere The layer of air that surrounds the earth.
77. lithosphere The solid mineral material that covers the earth.
78. hydrosphere All the water on the earth’s surface forms this.
79. Biosphere The layer of living things around the surface of the earth.
80. natural environment This is formed by all four spheres.
81. Ecology The study of living organisms and their interaction with the environment.
82. Ecosystem The environment of a community of plants and animals.
83. Earth quake Shaking of the earth’s crust caused by tectonic or volcanic action.
84. Drainage basin An area of land that drains precipitation into streams, rivers, and lakes.
85. environmental region This is formed by the combination of climate, soil, vegetation, and physical characteristics.
86. Low Pressure Zone A rising air mass that is light and warm.
87. High Pressure Zone A cold heavy mass of air that is falling.
88. Mountain barriers Mountains that block prevailing winds.
89. Temperate forest A region with naturally forested areas with fertile soil and four seasons usually agricultural or urban plus high population density.
90. Mediterranean forest A region with hot dry summers and warm moist winters usually agricultural with medium population
91. Temperate grassland A region of flat gently rolling land with soil for growing grain found in the interior of a continent experiencing four seasons plus medium population density.
92. Tropical rainforest A region with many species of plants and animals,that is very warm, and receives a lot of rainfall plus low population density.
93. Taiga or boreal A region in the northern hemisphere with long cold winters and short warm summers plus low precipitation.
94. Tundra A region that has long cold winters, permafrost plus low population density.
95. Polar A region with cold, dry, climate with glaciers considered unsuitable for human settlement.
96. Savanna A region with dry and wet seasons with tropical grassland plus low population
density.
97. Monsoon A region that is naturally forested with a wet and dry season that has been changed by rice cultivation plus high population density.
98. Desert A region with little precipitation that may be either hot or cold plus low population density.
99. ecocentric A view of the world that focuses on the importance of the natural environment instead of human interests.
100. 100.biodiversity The number and variety of organisms in a region.
101. 101. anthropocentric A view of the world where humans are the most important species.
102. sustainable Development that meets our current needs without risking future generations.
103. conservation Management of a region to protect it for future generations.
104. restoration ecology When an ecosystem is returned to its natural state before disturbed by man.
105. flood plain A flat broad river valley that floods regularly.
106. natural greenhouse effect The natural effect of the atmosphere to retain some energy/ heat from the sun.
107. radiation Energy/heat from the sun that reaches the earth’s surface.
108. average global temperature Temperature of the earth created by atmosphere and greenhouse gases (15 degrees Celsius).
109. global warming Human activities are adding greenhouse gases and causing the global temperature to rise.
110. desertification Expanding deserts into grasslands because of overgrazing livestock
111. air pollution Human activities creating toxic gases that cause lung diseases
112. carbon dioxide Greenhouse gas that is produced by human respiration and other technologies
113. monoculture Dependence on food that is genetically similar.
114. methane The natural greenhouse gas produced when plants are broken down by wetlands and animals.
115. chlorofluorocarbons A manmade gas that is created by refrigeration and aerosol cans.
116. ozone A kind of oxygen in the upper atmosphere that filters out harmful ultraviolet light from the sun.
117. acid rain Industry produces sulfur dioxide which is spread in the atmosphere and causes this problem.
118. growing season The length of time each year that the temperature is warm enough for plants to grow
Chapter 3 Definitions Review for Populations
119. Human Geography People and the places they live
120. Social Studies Human geography plus history
121. Natural Resource Anything in nature that people need or want
122. Globalization Changes that happen in a place because of technology and movement
123. Global Village The world seems smaller because communication technology connects everyone
124. Western Influence How cultures around the world are changing to be more like the west
125. economist* A person who studies how wealth is produced, consumed and distributed
126. demography Study of world populations
127. less developed world
(developing country) A country that is just beginning to industrialize
128. more developed world
(developed country) Countries with a good GDP and Standard of Living are called
129. standard of living How well people live
130. domestication Wild animals and plants that have been tamed by humans
131. Per Capita GDP* Gross Domestic Product divided by population is equal to
132. Exponential p63 A large growth in population in a short time
133. Sparse population Small number of people spread out over a large area
134. Emigration Movement of people out of a country
135. technology* Tools and ways of doing things
136. Population pyramid A graph that shows population distribution by age and gender
137. Zero population growth Population stays the same
138. replacement rate Number of children that must be born to keep population the same in a country
139. total fertility rate the sum of the age-specific birth rates
140. Internal migration People moving from place to place within a country
141. Crude Death Rate p64 Number of deaths per 1000 people
142. Rate of Natural Increase Number of crude births minus number of crude deaths
143. Demographer A person who studies population
144. demographic transition Four stages of birth and death rates as countries change from developing to developed
145. Gross Domestic Product Total value of all the goods and services
146. Census taker Person who collects information on who lives in a house or apartment (size of families).
147. Immigration Movement of people into a country
148. Cost of living The amount of money needed for basic needs such as food, clothing and shelter
149. Dense population Large number of people living in a small area
150. Human Development Index The UN creates a ranked list of the development of countries called
151. Crude birth rate* Number of babies born per 1000 people
152. Migration p73 Movement of people around the world
153. life expectancy The average number of years a person will live (effected by living conditions in a country
154. GDP per capita Gross Domestic Product divided by population is equal to
155. Exponential A large growth in population in a short time
156. Negative growth rate More deaths than births
157. Crude death rate Number of deaths per 1000 people
158. population density How many people live in a given area
159. colonialism One country having control of another usually in another
part of the world
160. Human rights The basic rights and freedoms to which all humans are entitled
social studies
Chapter 1 Terminology Name________________
1. -the time period lasting 1000 years between the 5th century and the 15th centuries
2. - points on the opposite sides of the earth.
3. - the imaginary line around the centre of the earth half way between the North and South poles( called 0 degrees latitude).
4. – the North and South points at either end of the earth’s axis.
5. - a tool to find direction used on maps (shows North, South, East and West).
6. – an imaginary line that goes through the centre of the earth between the North and South poles.
7. – the earth spinning on its axis.
8. - the movement of one planet around another planet/star
e.g. the Earth around the sun
9. – the path any planet follows around the sun
10. – every 4th year that has 366 days to make up for the previous 3 at 365 1/4 days.
11. – twice a year when the daylight hours equal the night hours.
12. – twice a year when either the daylight or nighttime are at their maximum.
13. – imaginary lines that run from East to West that are used the show distance from the equator.
14. -– imaginary lines that run from North to South that are used the show distance from the Prime Meridian.
15. – an imaginary line of longitude running from the North
poles to the South pole used to judge time and distance.
16. - an ancient tool for measuring time using the movement of the sun.
17. – are the system for keeping time around the world that has each hour of
the day equal to 15 degrees longitude.
18. – an imaginary line of longitude that is opposite the Prime Meridian.
19. – technology that uses information from satellites to find absolute location of people or things.
20. – ways of showing the earth ( a sphere) which is three dimensional as a flat
map which is two dimensional.
21. - any of the seven large land masses.
22. - land that is surrounded by water.
23. -a piece of land jutting out into the ocean from the mainland surrounded by
water on three sides.
24. - the surface features of the earth such as mountains, hills, plateaus and plains.
25. - a high rugged landform.
26. - a lower area of land formed by erosion that has elevated land on both sides.
27. -ia broad flat or gently rolling area of land.
28. - a broad flat or gently rolling area that is higher (elevated) above its
surroundings.
29. - the distance or height above sea level.
30. - a natural channel of water flowing toward a lake or ocean.
31. -a small stream flowing into a river which may flow into a lake or ocean.
32. - a body of water surrounded by land.
33. - formed when the ocean makes a large indent into land forming a semi-circle
34. - a narrow channel of water connecting two larger bodies of water.
35. - the name of a supercontinent that existed of 200 million years ago.
36. - the remains of plant or animal found in rock.
37. - a large piece of the Earth’s crust that can be bigger than a continent.
38. - a split in the Earth caused by tectonic plates pulling away from each other.
39. - the action of wearing away of the Earth’s surface by air, water and ice
40. - the relocation of soil and pieces of rock that were worn or carried
away by wind, ice, and water.
41. – small pieces of soil and rock carried by water.
42. - a triangular shaped deposit of soil and sand at the mouth of a river.
43. - a gigantic body of ice that is found in mountain and polar regions.
44. - study of our world
45. -person who describes and analyzes the human and physical characteristics of the world
46. -the exact location of something on the earth using coordinates of latitude and longitude
47. - the ratio between the real distance and the distance on a map
48. technology to display and store facts about the physical world
Chapter 2 and 19 Terminology Definitions Review for Climate and Sustainable Development
49. The study of the natural features of the earth
50. A half-sphere view of the earth created by geographers to identify a large part of the earth e.g. northern, southern, eastern or western
51. A particular land surface feature, such as a mountain, hill, plateau, or plain
52. An elevated piece of land
53. Water flowing by continents which either warm or cool the land based on their temperature.
54. Outward explosion of the earth’s molten inner core caused by tectonic forces
55. The day to day temperature and precipitation found anywhere in the world.
56. Climate located from 30 to 60 degrees latitude North or South of the equator.
57. Winds that blow in a specific pattern around the earth.
58. When there is a lot of moisture in the air.
59. Water vapor from plants.
60. Very dry, little or no precipitation.
61. Permanently frozen ground, about 1 meter beneath the surface.
62. A large body of air covering a large distance.
63. Water (in any form) falling to Earth.
64. Pattern of weather in a particular place measured over at least 30 years.
65. Climate located from 0 to 30 degrees latitude North or South of the equator.
66. The name of the cycle of water through land, water and air.
67. Water vapor changes from a gas to a liquid.
68. An invisible gas created when water evaporates.
69. Mountain slopes that face away from the prevailing wind.
70. A circular path a planet like Earth takes around the sun.
71. The height of any part of the earth above sea level.
72. Water changes into a vapor or gas.
73. Climate located from 60 to 90 degrees latitude North or South of the equator.
74. Area between the Tropic of Cancer and Tropic of Capricorn.
75. Mountain slopes that face the prevailing winds.
76. The layer of air that surrounds the earth.
77. The solid mineral material that covers the earth.
78. All the water on the earth’s surface forms this.
79. The layer of living things around the surface of the earth.
80. This is formed by all four spheres.
81. The study of living organisms and their interaction with the environment.
82. The environment of a community of plants and animals.
83. Shaking of the earth’s crust caused by tectonic or volcanic action.
84. An area of land that drains precipitation into streams, rivers, and lakes.
85. This is formed by the combination of climate, soil, vegetation, and physical characteristics.
86. A rising air mass that is light and warm.
87. A cold heavy mass of air that is falling.
88. Mountains that block prevailing winds.
89. A region with naturally forested areas with fertile soil and four seasons usually agricultural or urban plus high population density.
90. A region with hot dry summers and warm moist winters usually agricultural with medium population
91. A region of flat gently rolling land with soil for growing grain found in the interior of a continent experiencing four seasons plus medium population density.
92. A region with many species of plants and animals,that is very warm, and receives a lot of rainfall plus low population density.
93. A region in the northern hemisphere with long cold winters and short warm summers plus low precipitation.
94. A region that has long cold winters, permafrost plus low population density.
95. A region with cold, dry, climate with glaciers considered unsuitable for human settlement.
96. A region with dry and wet seasons with tropical grassland plus low population
density.
97. A region that is naturally forested with a wet and dry season that has been changed by rice cultivation plus high population density.
98. A region with little precipitation that may be either hot or cold plus low population density.
99. A view of the world that focuses on the importance of the natural environment instead of human interests.
100. The number and variety of organisms in a region.
101. A view of the world where humans are the most important species.
102. Development that meets our current needs without risking future generations.
103. Management of a region to protect it for future generations.
104. When an ecosystem is returned to its natural state before disturbed by man.
105. A flat broad river valley that floods regularly.
106. The natural effect of the atmosphere to retain some energy/ heat from the sun.
107. Energy/heat from the sun that reaches the earth’s surface.
108. Temperature of the earth created by atmosphere and greenhouse gases (15 degrees Celsius).
109. Human activities are adding greenhouse gases and causing the global temperature to rise.
110. Expanding deserts into grasslands because of overgrazing livestock
111. Human activities creating toxic gases that cause lung diseases
112. Greenhouse gas that is produced by human respiration and other technologies
113. Dependence on food that is genetically similar.
114. The natural greenhouse gas produced when plants are broken down by wetlands and animals.
115. A manmade gas that is created by refrigeration and aerosol cans.
116. A kind of oxygen in the upper atmosphere that filters out harmful ultraviolet light from the sun.
117. Industry produces sulfur dioxide which is spread in the atmosphere and causes this problem.
118. The length of time each year that the temperature is warm enough for plants to grow
Chapter 3 Definitions Review for Populations
119. People and the places they live
120. Human geography plus history
121. Anything in nature that people need or want
122. Changes that happen in a place because of technology and movement
123. The world seems smaller because communication technology connects everyone
124. How cultures around the world are changing to be more like the west
125. A person who studies how wealth is produced, consumed and distributed
126. Study of world populations
127. A country that is just beginning to industrialize
128. Countries with a good GDP and Standard of Living are called
129. How well people live
130. Wild animals and plants that have been tamed by humans
131. Gross Domestic Product divided by population is equal to
132. A large growth in population in a short time
133. Small number of people spread out over a large area
134. Movement of people out of a country
135. Tools and ways of doing things
136. A graph that shows population distribution by age and gender
137. Population stays the same
138. Number of children that must be born to keep population the same in a country
139. the sum of the age-specific birth rates
140. People moving from place to place within a country
141. Number of deaths per 1000 people
142. Number of crude births minus number of crude deaths
143. A person who studies population
144. Four stages of birth and death rates as countries change from developing to developed
145. Total value of all the goods and services
146. Person who collects information on who lives in a house or apartment (size of families).
147. Movement of people into a country
148. The amount of money needed for basic needs such as food, clothing and shelter
149. Large number of people living in a small area
150. The UN creates a ranked list of the development of countries called
151. Number of babies born per 1000 people
152. Movement of people around the world
153. The average number of years a person will live (effected by living conditions in a country
154. Gross Domestic Product divided by population is equal to
155. A large growth in population in a short time
156. More deaths than births
157. Number of deaths per 1000 people
158. How many people live in a given area
159. One country having control of another usually in another
part of the world
160. The basic rights and freedoms to which all humans are entitled
Monday, June 6, 2011
Measures of Central Tendency
Notes for June 06, 2011



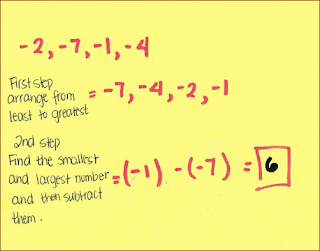
Math Notes
- A value that represents the centre of a data set
-It can be Mean, Medium or Mode
-A data set is a group of numbers that you must arrange in order from least to greatest.

Median- the middle number in a set of data after the data have been arranged in order

If this^ happens, all you have yo do is find out what number is in between the two numbers. So take 6 and 8, You know that 7 is in between so, 7 is our median. Another way to find out the median...
Take the two middle numbers (6 and 8) add them together (6+8) and that would equal 14 right? So, you take 14, and divide it by 2 (14÷2) and that would equal 7, and seven (7) is our Median.

If this^ happens, remember the first thing you do when you get a data, you have to arrange them from least to greatest, after you do that and you get two numbers in the middle and you wanted to find out the Median, remember: take the two middle numbers (3 and 10) add them together (3+10) and that would equal 13 right? So, you take 13, and divide it bye 2 (13÷2) and that would equal 13, and thirteen (13) is our Median.
Mode- the most frequent occuring in a set of data. Here is how you can remember the meaning, MODE and MOST have both 4 letters and they both start in "MO".
(e.g) 3,5,7,7,9
the Mode would be "7" because it's the most occuring number, there are two of them and only one the other numbers.
(e.g) 2,2,4,6,6,8,11
the Mode would be 2 and 6, because there are two and them and they are both tied for having two numbers.
(e.g) 1,1,1,2,2,2,3,3,3
the Mode is nothing because there are three of them for each number.
(e.g) 1,1,1,2,2,2,3,3,3,4
If this happens, the mode this time would be 1,2 and 3, because they are all tied for being first.
Mean- A measure of central tendency. Th sum of a set of values divided by the number of values in the set.

The Mean in this^ image is 6, because the data states 4, 6, and 8, So you take all the numbers in the data (4, 6, and 8) and then add them up (4+6+8) and then that would equal 18 right? So, take 18 and divide it by how much numbers there are in the data, In this data there are 3 numbers, (18÷3) and that would equal to 6, So 6 is our Mean.
Range- The positive difference between the largest and smallest values in a data set.

If this^ happens, always remember when you get a data set, you have to order them from least to greatest, after you do that you take the biggest number (in this situation it's #9) and the smallest number (in this situation it's the #1) and subtract the biggest number to the smallest number (9-1=8) and that would equal to 8, so 8 is our Range.
Outlier- A value that is much longer or smaller than the other data value, the data set may have more than 1 outlier or zero outliers.
The outliers for 1,67,68,67,64,65,100 would be 1 and 100, because the rest of the numbers are somewhere in the 60's and 1 and 100 are so far off.
MATH HOMEWORK FOR TODAY:
Find out the Mean, Mode, Range, Outliers, for the following data set.
1.) 18,19,79,17,20,12
2.)14,14,16,15,1,16
3.)98,202,99,91,2,95,89,88,94
*Here is a LINK where you can learn more facts about Measures of Central Tendency.
*Here is also a link to a VIDEO about Mean, Median and Mode.
Sunday, June 5, 2011
Math Notes
You might want to review some of them if you're having trouble.
I also added examples for most of them.
The images below explains Variables, Expressions, Value, Constant and Numerical Coefficient.



Notes for June 1
Equation- mathematical statement with two expressions that have the same value.
Model 8 times a number plus 4 is 12
8n+4=12
I.D= Identify 5y-6=19
variable- y
number coefficient- 5
constant- (-6)
Opposite operation
+,-
x, division
-,+
division, x
need more help?
Saturday, June 4, 2011
Math Notes



*If you're having trouble with this^ example, here is a video about SUBTRACTING integers. If you also would like to see a video about ADDING integers, here is another one.
Here is also a WEBSITE about equations.
*These were the notes we took down on Friday, I'm sorry if I posted it a little late.
HOMEWORK: Finish homework booklet pages 134-139.. and finish Chapter Review and Practice Test in our TEXTBOOK.
Friday, June 3, 2011
Notes for May 19, May 27, and June 1





Thursday, June 2, 2011
notes, june 1/2 2011
Variable-(j is the variable) a letter that represent a unknown number.
Expression-(2j x 3) any single number or variable or a combination of operations.
Constant-(3 is the constant) a number that does not change, increases or decreases, the value of an expression.
Numerical coefficient-(2 is the numerical coefficient) a number that multiply a variable.
Equation- mathematical statement with two expression that have the same value. (a scale)
eg. x+3=3 , y-7=(4) , 3a-2=a+2 , b=4
Identify the value of variable.
Subtract - Add
Multiply - Divide
Divide - Multiply
Remember, when did something on the left side you have to do the same thing in the right side.
Remember to always check your answer.
Math notes for June 2, 2011
A+4=10
6+4=10
10=10
Use reverse order of operation, what you do the first one, you have to do to the other. (As you can see when we used reverse order of operation the first time, we also did the same at the end)

Here are some other practices we did:

CHECK:
B-2=5
7-2=5
5=5

CHECK:
3c=21
3x7=21
c=7

CHECK:
2j+1=9
2(4)+1=9
8+1=9
9=9

CHECK:
f÷3-2=1
9÷3-2=1
3-2=1
1=1
Here is a LINK where you can practice with algebra.
Here is also a VIDEO about equations.
*I was having trouble with the video, so just click the link and you will get to it! :)








